Diagnosis
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): The first thing we do is an ECG to see the electrical signal of the heart. It shows changes if you are having or had a heart attack. But even with normal ECG patients may have a chance of heart disease.
- Blood tests: this is the most reliable test. We do troponin I, which is a heart protein that releases into the blood during a heart attack.
- Chest X-ray: We can see the size and shape of the heart.
- Echocardiogram: This can identify which part of the heart is damaged or affected.
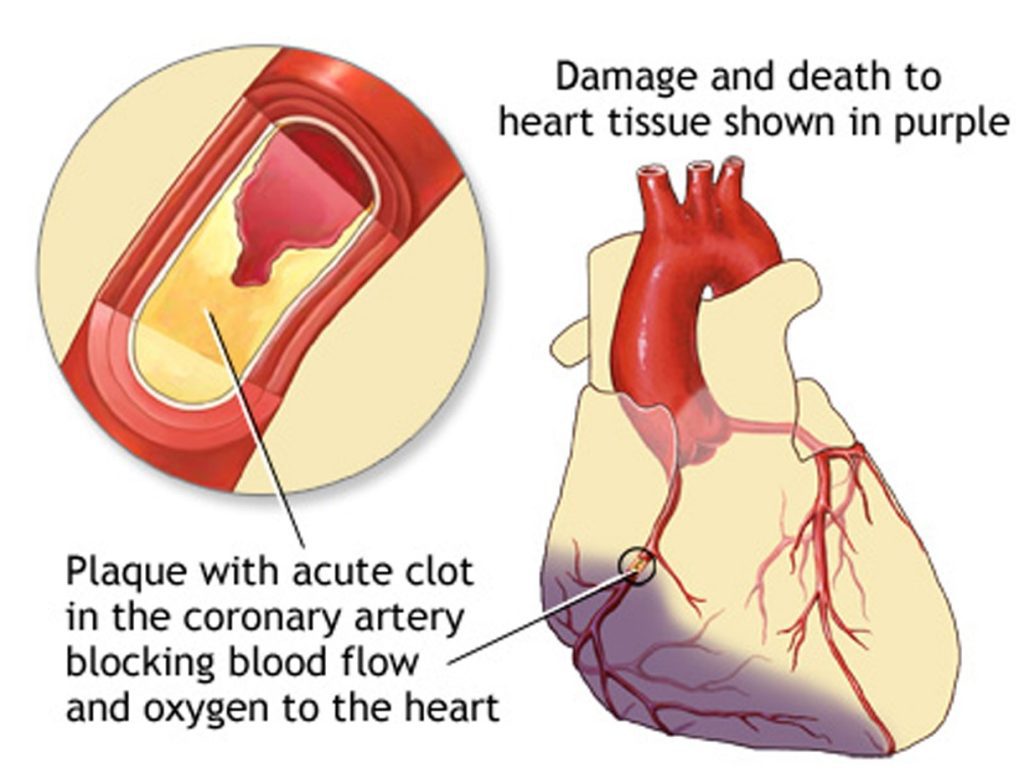
- Coronary angiography: through this procedure we can see the percentage of blockage of arteries.
Treatment
- Medications: if blockage of heart vessels is not significant, the doctor will use some medication that will help to reduce the blockage of arteries.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI): By using a balloon, the doctor will dilate the coronary artery and place a stent/ring in the blockage area so that blood can pass through the vessel easily. This treatment is available in Cardiology Department.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): by doing this surgery, the doctor will create a path for blood to flow into the heart. This treatment is available in Cardiovascular Department.
If anyone is having a heart attack, please immediately go to the hospital because they need emergency medical help immediately. Doctors may perform an AMI test to diagnose the condition and begin treatment. Remember, immediate measures can save lives and also reduce the damage to the heart.